What is SCADA used for?
SCADA, short for Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition, plays a vital role in managing and monitoring critical infrastructure across various industries. Imagine it as the brain and nervous system of power grids, pipelines, factories, and more. SCADA systems gather real-time data (like temperature, pressure, or flow rates) from sensors and equipment, analyze it for anomalies, and control operations remotely or on-site. This allows for efficient operation, quick response to issues, and improved safety. Think of SCADA as the unseen hero keeping the lights on, water flowing, and production lines humming!
Introduction to SCADA
SCADA systems comprise hardware and software components designed to supervise and manage industrial processes. These systems play a pivotal role in critical infrastructure sectors such as energy, water, transportation, and manufacturing. Also, read about the SAP Agile Methodology
Components of SCADA
Remote Terminal Units (RTUs)
RTUs are devices that collect data from sensors and equipment located in remote sites. They transmit this data to the central SCADA system for analysis and control.
Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs)
PLCs are industrial computers programmed to automate specific tasks or processes. They interface with sensors and actuators to control machinery and equipment based on predefined logic.
Human-machine interface (HMI)
HMIs provide a graphical interface for operators to interact with the SCADA system. They display real-time data, alarms, and controls, allowing operators to monitor and manage processes effectively.
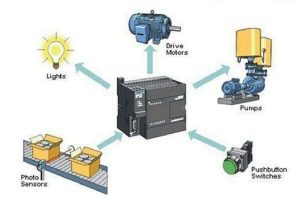
How SCADA works
SCADA systems collect data from various sensors and devices distributed throughout a facility. This data is transmitted to the central SCADA server, where it is processed and presented to operators in a comprehensible format. Operators can then analyze the data and take appropriate actions to optimize processes and ensure safety. Discover more about How to Factory Reset HP Laptop
Industries where SCADA is used
Oil and gas
SCADA systems are widely used in the oil and gas industry to monitor and control drilling operations, pipeline networks, and refinery processes.
Energy and utilities
In the energy sector, SCADA systems help manage power generation, transmission, and distribution infrastructure. They enable utilities to optimize energy production, detect faults, and respond to grid disturbances promptly.
Manufacturing
SCADA systems play a vital role in manufacturing plants by monitoring production processes, managing inventory, and ensuring quality control. They help improve efficiency, reduce downtime, and enhance product consistency.
Benefits of SCADA
Improved efficiency
By providing real-time visibility into processes, SCADA systems help identify inefficiencies and optimize operations. This leads to increased productivity and reduced operating costs.
Enhanced safety
SCADA systems enable operators to monitor equipment conditions and detect potential hazards remotely. They can implement safety protocols and shutdown procedures quickly to prevent accidents and protect personnel.
Cost savings
Through predictive maintenance and optimized resource utilization, SCADA systems help companies save money by reducing downtime, minimizing waste, and extending equipment lifespan.
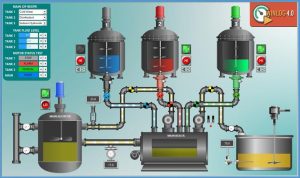
Challenges of SCADA
Security concerns
As SCADA systems become more interconnected, they become vulnerable to cyber threats and attacks. Ensuring the security of these systems is crucial to protect critical infrastructure and prevent unauthorized access or manipulation of data.
Integration issues
Integrating SCADA systems with existing infrastructure and legacy equipment can be complex and challenging. Compatibility issues and interoperability constraints may arise, requiring careful planning and implementation.
Maintenance requirements
SCADA systems require regular maintenance and updates to ensure optimal performance and reliability. This includes software patches, hardware upgrades, and periodic testing to identify and address potential issues proactively.
Future trends in SCADA
Integration with IoT
The integration of SCADA systems with the Internet of Things (IoT) enables enhanced connectivity and data exchange between devices and sensors. This allows for more extensive monitoring and control capabilities, as well as predictive analytics and condition-based maintenance.
Cloud-based SCADA systems
Cloud-based SCADA solutions offer scalability, flexibility, and accessibility advantages over traditional on-premises systems. They enable remote monitoring and management from any location with an internet connection, facilitating real-time decision-making and collaboration.
Advanced analytics
With the advent of big data and machine learning technologies, SCADA systems can leverage advanced analytics to derive actionable insights from vast amounts of data. Predictive analytics algorithms can forecast equipment failures, optimize energy usage, and improve process efficiency.
Conclusion
In conclusion, SCADA systems play a vital role in modern industries by providing real-time monitoring, control, and optimization capabilities. They enable companies to improve efficiency, enhance safety, and reduce costs, making them indispensable tools for managing complex industrial processes.
FAQs
What does SCADA stand for?
SCADA stands for Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition.
Which industries use SCADA systems?
SCADA systems are used in industries such as oil and gas, energy and utilities, and manufacturing.
What are the benefits of SCADA?
The benefits of SCADA include improved efficiency, enhanced safety, and cost savings through predictive maintenance and optimized resource utilization.
What are the challenges of implementing SCADA systems?
Challenges of implementing SCADA systems include security concerns, integration issues, and maintenance requirements.
What are the future trends in SCADA?
Future trends in SCADA include integration with IoT, adoption of cloud-based solutions, and leveraging advanced analytics for predictive maintenance and optimization.
